Actualizar LinuxCNCa una nueva versión menor (es decir, a una nueva versión en la misma serie estable, por ejemplo de 2.9.1 a 2.9.2) es un proceso automático si su PC esta conectada a internet . Verá un mensaje de actualización después del lanzamiento de una version menor nueva, junto con otras actualizaciones de software. Si no tiene internet en su PC vea Actualizando sin red.
1. Upgrade to the new version
This section describes how to upgrade LinuxCNC from version 2.8.x to a 2.9.y version. It assumes that you have an existing 2.8 install that you want to update.
To upgrade LinuxCNC from a version older than 2.8, you have to first upgrade your old install to 2.8, then follow these instructions to upgrade to the new version.
If you do not have an old version of LinuxCNC to upgrade, then you’re best off making a fresh install of the new version as described in the section Getting LinuxCNC.
Mas aún, si ejecuta Ubuntu Precise o Debian Wheezy vale la pena considerar hacer un respaldo del directorio "linuxcnc" en un medio extraible y realizar una instalación limpia de una versión mas reciente de SO y LinuxCNC ya que esas versiones terminaron su ciclo de vida en 2017 y 2018 respectivamente. Si esta ejecutando en Ubuntu Lucid entonces tendrá que hacer esto, ya que Lucid ya no es soportada por LinuxCNC (su ciclo de vida terminó en 2013).
To upgrade major versions like 2.8 to 2.9 when you have a network connection at the machine you need to disable the old linuxcnc.org apt sources in the file /etc/apt/sources.list and add a new linuxcnc.org apt source for 2.9, then upgrade LinuxCNC.
The details will depend on which platform you’re running on. Open a terminal then type lsb_release -ic to find this information out:
lsb_release -ic
Distributor ID: Debian
Codename: BusterYou should be running on Debian Buster, Bullseye or Bookworm or Ubuntu 20.04 "Focal Fossa" or newer. LinuxCNC 2.9.y will not run on older distributions than these.
You will also need to check which realtime kernel is being used:
uname -r
6.1.0-10-rt-amd64Si ve (como arriba) -rt- en el nombre del kernel, entonces está ejecutando el preempt-rt kernel y debería instalar la versión "uspace" de LinuxCNC. También debe instalar uspace para configuraciones "sim" en kernels que no son en tiempo real.
If you see -rtai- in the kernel name then you are running RTAI realtime. See below for the LinuxCNC version to install. RTAI packages are available for Bookworm and Buster but not currently for Bullseye.
1.1. Apt Sources Configuration
-
Open the
Software Sourceswindow. The process for doing this differs slightly on the three supported platforms:-
Debian:
-
Haga clic en
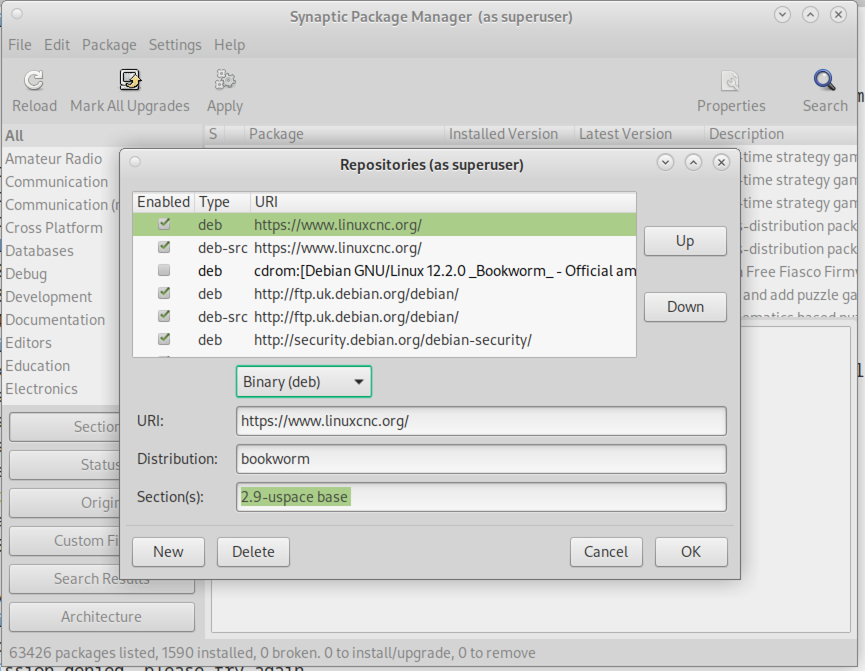
Menú de aplicaciones, luego enSistema, luego enAdministrador de paquetes Synaptic. -
In Synaptic, click on the
Settingsmenu, then clickRepositoriesto open theSoftware Sourceswindow.
-
-
Ubuntu Precise:
-
Click on the
Dash Homeicon in the top left. -
In the
Searchfield, type "software", then click on theUbuntu Software Centericon. -
In the Ubuntu Software Center window, click on the
Editmenu, then click onSoftware Sources...to open theSoftware Sourceswindow.
-
-
Ubuntu Lucid:
-
Click the
Systemmenu, thenAdministration, thenSynaptic Package Manager. -
In Synaptic, click on the
Settingsmenu, then click onRepositoriesto open theSoftware Sourceswindow.
-
-
-
In the
Software Sourceswindow, select theOther Softwaretab. -
Delete or un-check all the old linuxcnc.org entries (leave all non-linuxcnc.org lines as they are).
-
Click the
Addbutton and add a new apt line. The line will be slightly different on the different platforms:
| OS / Realtime Version | Repository |
|---|---|
Debian Buster - preempt |
|
Debian Buster - RTAI |
|
Debian Bullseye - preempt |
|
Debian Bookworm - preempt |
|
Debian Bookworm - RTAI |
|
-
Click
Add Source, thenClosein the Software Sources window. If it pops up a window informing you that the information about available software is out-of-date, click theReloadbutton.
1.2. Upgrading to the new version
Ahora su computadora sabe dónde obtener la nueva versión del software. A continuación tenemos que instalarlo.
The process again differs depending on your platform.
1.2.1. Debian Buster, Bullseye and Bookworm
Debian uses the Synaptic Package Manager.
-
Open Synaptic using the instructions in Setting apt sources above.
-
Click the
Reloadbutton. -
Use the Search function to search for
linuxcnc. -
The package is called "linuxcnc" for RTAI kernels and "linuxcnc-uspace" for preempt-rt.
-
Click the check box to mark the new linuxcnc and linuxcnc-doc-* packages for upgrade. The package manager may select a number of additional packages to be installed, to satisfy dependencies that the new linuxcnc package has.
-
Click the
Applybutton, and let your computer install the new package. The old linuxcnc package will be automatically upgraded to the new one.
1.3. Ubuntu
-
Click on the
Dash Homeicon in the top left. -
In the
Searchfield, type "update", then click on theUpdate Managericon. -
Click the
Checkbutton to fetch the list of packages available. -
Click the
Install Updatesbutton to install the new versions of all packages.
2. Updating without Network
Para actualizar sin una conexión de red, necesita descargar un paquete .deb y luego instalarlo con dpkg. Los .deb se pueden encontrar en https://linuxcnc.org/dists/ .
Tiene que profundizar en el enlace anterior para encontrar el deb correcto para su instalación. Abra una terminal y escriba lsb_release -ic para encontrar el nombre de su sistema operativo.
> lsb_release -ic
Distributor ID: Debian
Codename: bullseyePick the OS from the list then pick the major version you want like 2.9-rt for RTAI or 2.9-rtpreempt or 2.9-uspace for preempt-rt.
Next pick the type of computer you have: binary-amd64 for any 64-bit x86, binary-i386 for 32 bit, binary-armhf (32bit) or binary-arm64 (64bit) for Raspberry Pi.
A continuación, elija la versión que desee de la parte inferior de la lista como linuxcnc-uspace_2.8.0_amd64.deb (elija la más reciente por su fecha). Descargue el deb y cópielo a su directorio de usuario. Puede cambiar el nombre del archivo a algo un poco más corto con el administrador de archivos, como linuxcnc_2.8.0.deb. Luego abra una terminal e instálelo con el gestor de paquetes con este comando:
sudo dpkg -i linuxcnc_2.9.2.deb3. Updating Configuration Files for 2.9
3.1. Stricter handling of pluggable interpreters
If you just run regular G-code and you don’t know what a pluggable interpreter is, then this section does not affect you.
A seldom-used feature of LinuxCNC is support for pluggable interpreters, controlled by the undocumented [TASK]INTERPRETER INI setting.
Versions of LinuxCNC before 2.9.0 used to handle an incorrect [TASK]INTERPRETER setting by automatically falling back to using the default G-code interpreter.
Since 2.9.0, an incorrect [TASK]INTERPRETER value will cause LinuxCNC to refuse to start up. Fix this condition by deleting the [TASK]INTERPRETER setting from your INI file, so that LinuxCNC will use the default G-code interpreter.
3.2. Canterp
If you just run regular G-code and you don’t use the canterp pluggable interpreter, then this section does not affect you.
In the extremely unlikely event that you are using canterp, know that the module has moved from /usr/lib/libcanterp.so to /usr/lib/linuxcnc/canterp.so, and the [TASK]INTERPRETER setting correspondingly needs to change from libcanterp.so to canterp.so.
4. Updating Configuration Files (for 2.10.y)
Touchy: the Touchy MACRO entries should now be placed in a [MACROS] section of the INI rather than in the [TOUCHY] section. This is part of a process of commonising the INI setting between GUIs.